

Under this viewpoint, throughput is more important than gross margin, as is the utilization level of the bottleneck operation in a company. A high rate of inventory turnover combined with a low gross margin is the equivalent of a low rate of turnover with a high gross margin, from the perspective of total annual return on investment.Ī strong case can be made that gross margin is not useful, since it does not focus on the ability of a company's production system as a whole to create throughput (which is sales minus totally variable expenses). Gross margin analysis should be accompanied by a consideration of the rate at which inventory turns over. Because of the overhead cost inclusion, gross margin is not the same as contribution margin (which only reduces sales by the amount of any variable expenses incurred). Gross margin includes an allocation of factory overhead costs, some of which may be fixed costs or mixed costs. A decline in the gross margin percentage may be cause for considerable concern, since it can imply a decline in the competitiveness of a company's products and/or services in the marketplace. The gross margin percentage is useful when tracked on a trend line, to see if there are any significant changes that may require further investigation.
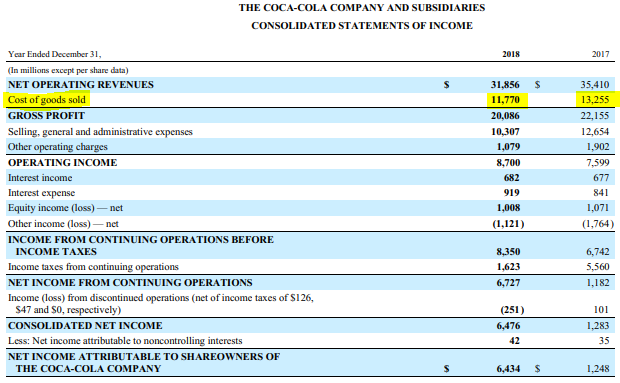
The gross margin percentage may be stated in a company's income statement. (Net sales - Cost of goods sold) / Net salesįor example, a company has sales of $1,000,000 and cost of goods sold of $750,000, which results in a gross margin of $250,000 and a gross margin percentage of 25%. Gross margin is frequently expressed as a percentage, called the gross margin percentage. It is better to use net sales than gross sales, since a large number of deductions from gross sales could skew the results of the calculation. Gross Margin FormulaĪs just noted, the formula for the gross margin is net sales less the cost of goods sold. It is a key concern in the derivation of a budget, since it drives the amount of expenditures that can be made in these additional expense classifications. The amount of gross margin earned by a business dictates the level of funding left with which to pay for selling and administrative activities and financing costs, as well as to generate a profit. Conversely, the sale of a physical product, such as an automobile, will result in a much lower gross margin.

For example, a company that sells electronic downloads through a website may have an extremely high gross margin, since it does not sell any physical goods to which a cost might be assigned. The figure can vary dramatically by industry. The gross margin reveals the amount that a business earns from the sale of its products and services, before the deduction of any selling and administrative expenses. Gross margin is a company’s net sales minus its cost of goods sold.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
